eBPF AF_XDP学习
官方教程地址(19年版本,有些旧,包依赖关系已经发生了变化):https://github.com/xdp-project/xdp-tutorial
What is AF_XDP?
AF_XDP是一个为高性能数据包处理而优化的解决方案
使用XDP程序中的XDP_REDIRECT动作,该程序可以使用bpf_redirect_map()函数将入帧重定向到其他支持XDP的netdev。AF_XDP socket使XDP程序能够将帧重定向到用户空间应用程序中的内存缓冲区,从而在用户态对数据包进行各种处理
1)XDP程序Easy Example
下列程序可以用于在遭受DDos攻击时使用,作用是丢弃所有网络数据包(不要随意在实际网卡跑这个程序,当此程序加载成功的瞬间,ssh链接就会失效,然后就只能重启服务器了):
XDP内核程序,会被编译为.o文件
1 |
|
加载XDP bpf模块的核心程序:
1 | int xdp_link_attach(int ifindex, __u32 xdp_flags, int prog_fd) |
在libbpf中,可以直接使用libbpf提供的加载工具函数进行加载。
2)XDP内核程序参数
XDP输出参数:
1 | enum xdp_action { |
XDP输入参数:
data和data_end字段分别是数据包开始和结束的指针,它们是用来获取和解析传来的数据,第三个值是data_meta指针,初始阶段它是一个空闲的内存地址,供XDP程序与其他层交换数据包元数据时使用。最后两个字段分别是接收数据包的接口和对应的RX队列的索引。当访问这两个值时,BPF代码会在内核内部重写,以访问实际持有这些值的内核结构struct xdp_rxq_info。
1 | struct xdp_md { |
3)Libbpf中使用AF_XDP
由于现在libbpf已经停止了对AF_xdp socket(xsk)的直接支持,为了方便,直接在libpbf项目中手动引入XDP-TOOL,以获取xdp全部功能
https://github.com/libbpf/libbpf/commit/277846bc6c15b603c8fdfbd757700443c95a4a96
XDP tools: https://github.com/xdp-project/xdp-tools
步骤如下:
将xdp-tools包加入libbpf项目目录
修改makefile,对xdp-tools进行编译链接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16#加入编译xdp-tool的部分
XDPTOOL_SRC := $(abspath ../../xdp-tools) #待编译文件
LIBXDP_SOURCES := $(wildcard $(XDPTOOL_SRC)/lib/libxdp/libxdp*.[ch]) $($(XDPTOOL_SRC)/lib/libxdp/xsk.c)
XDPTOOL := $(abspath $(OUTPUT)/libxdp.a)
$(XDPTOOL): $(LIBXDP_SOURCES)
$(call msg,LIB,$@)
$(Q)$(MAKE) -C $(XDPTOOL_SRC) BUILD_STATIC_ONLY=1 \
OBJDIR=$(dir $@)/xdptool DESTDIR=$(dir $@) \
INCLUDEDIR= LIBDIR= UAPIDIR= \
libxdp_install
# 最后生成可执行文件时,链接xdp-tool
$(APPS): %: $(OUTPUT)/%.o $(XDPTOOL) $(LIBBPF_OBJ)| $(OUTPUT)
$(call msg,BINARY,$@)
$(Q)$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $^ $(ALL_LDFLAGS) -lpthread -lelf -lz -o $@在用户态bpf程序中引入 #include <xdp/xsk.h>,后续即可使用AF_XDP的功能
利用Libbpf中的帮助函数attach xdp程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12// 获取全部网卡信息的工具函数
// 参考此博客 https://blog.csdn.net/Rong_Toa/article/details/109118585
int ret = get_ifinfo(ifdisplay, NULL);
// Attack bpf sec to all IF devs
for(int i=0;i<ret;i++){
bpf_program__attach_xdp (skel->progs.xdp_prog, i);
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to attach BPF skeleton\n");
goto cleanup;
}
}
经过测试,可以在pipe中看到XDP包的信息
4)利用AF XDP将数据包redirect到用户态
参考资料:
https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/next/networking/af_xdp.html
https://blog.cloudflare.com/a-story-about-af-xdp-network-namespaces-and-a-cookie/
AF_XDP用户态与内核交换数据包原理:
AF_XDP在在用户和内核之间,声明了一块公共的内存区域:UMEM。xdp内核程序会将xdp数据包存储在UMEM里,
同时有四种ring:FILL, COMPLETION, RX , TX。内核将指向UMEM中数据包的指针放入RX queue里。供用户空间消费。同时用户态可以通过写入TX queue,将数据包传回内核处理。内核处理该数据包之后,将TX描述符放入completion queue里,表示处理完成。最后用户空间可以在Fill queue或TX队列里回收描述符。
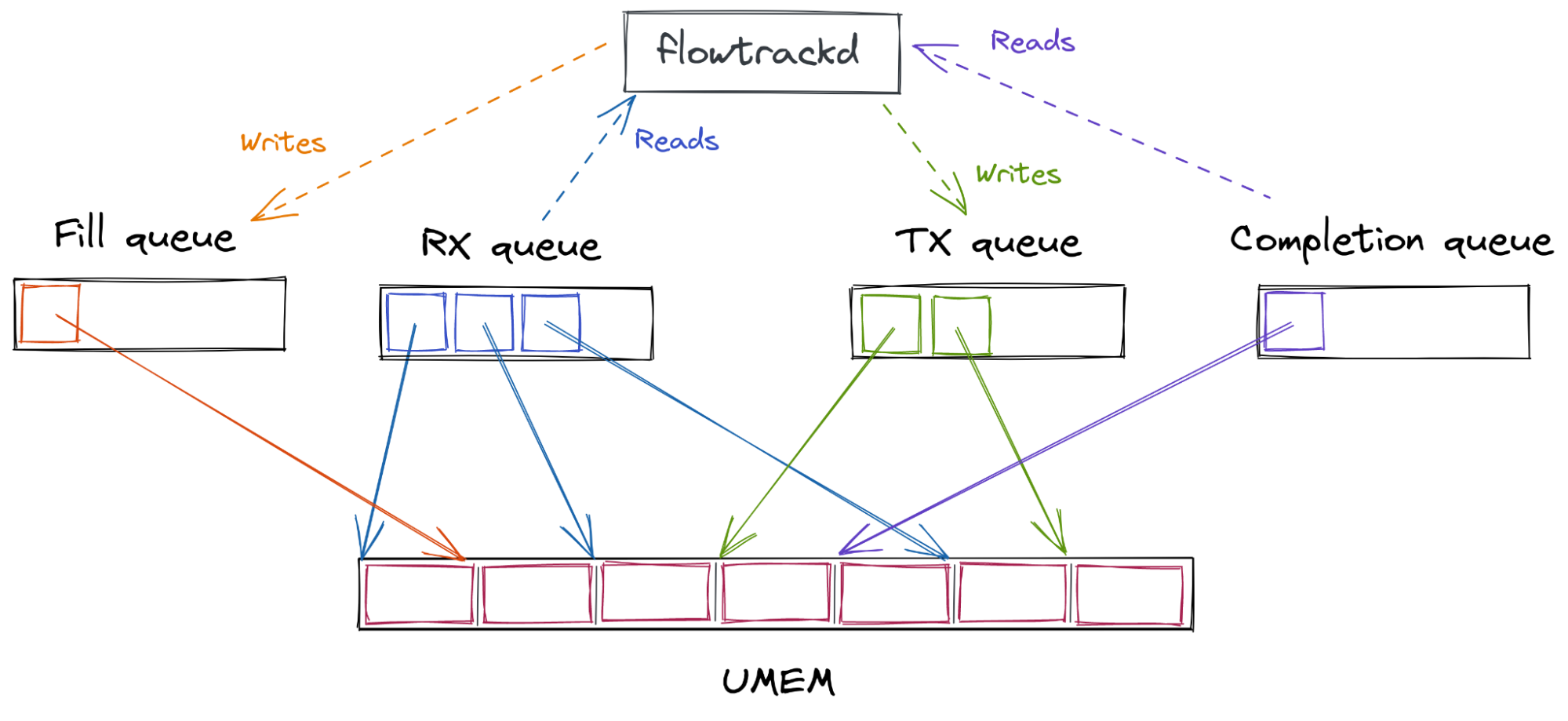
一张很有启发意义的图:
5)AF_XDP代码详解
分配和初始化UMEM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37struct xsk_umem_info {
struct xsk_ring_prod fq;
struct xsk_ring_cons cq;
struct xsk_umem *umem;
void *buffer;
};
struct xsk_umem_info *umem;
void *packet_buffer;
uint64_t packet_buffer_size = NUM_FRAMES * FRAME_SIZE;
// 进行内存对齐
posix_memalign(&packet_buffer,
getpagesize(), /* PAGE_SIZE aligned */
packet_buffer_size)
// 初始化UMEM
umem = configure_xsk_umem(packet_buffer, packet_buffer_size);
// configure_xsk_umem 函数定义
static struct xsk_umem_info *configure_xsk_umem(void *buffer, uint64_t size)
{
struct xsk_umem_info *umem;
int ret;
// 声明一块内存空间
umem = calloc(1, sizeof(*umem));
if (!umem)
return NULL;
// 进行umeme创建
ret = xsk_umem__create(&umem->umem, buffer, size, &umem->fq, &umem->cq,
NULL);
if (ret) {
errno = -ret;
return NULL;
}
//
umem->buffer = buffer;
return umem;
}开启AF_XDP socket (xsk)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78struct xsk_socket_info *xsk_socket;
xsk_socket = xsk_configure_socket(umem);
// 该函数写死了部分参数,实际使用应通过变量传入这些参数
static struct xsk_socket_info *xsk_configure_socket(struct xsk_umem_info *umem)
{
struct xsk_socket_config xsk_cfg;
struct xsk_socket_info *xsk_info;
uint32_t idx;
uint32_t prog_id = 0;
int i;
int ret;
xsk_info = calloc(1, sizeof(*xsk_info));
if (!xsk_info)
return NULL;
xsk_info->umem = umem;
xsk_cfg.rx_size = XSK_RING_CONS__DEFAULT_NUM_DESCS;
xsk_cfg.tx_size = XSK_RING_PROD__DEFAULT_NUM_DESCS;
xsk_cfg.libbpf_flags = 0;
xsk_cfg.xdp_flags = 0; //***
xsk_cfg.bind_flags = 0; //***
/*!
* int xsk_socket__create(
* struct xsk_socket **xsk,
* const char *ifname,
* __u32 queue_id,
* struct xsk_umem *umem,
* struct xsk_ring_cons *rx,
* struct xsk_ring_prod *tx,
* const struct xsk_socket_config *config);
*/
// 指定将Af_XDP附加在veth-adv03网卡上
ret = xsk_socket__create(&xsk_info->xsk, "veth-adv03",
0, umem->umem, &xsk_info->rx,
&xsk_info->tx, &xsk_cfg);
if (ret)
goto error_exit;
// 判断是否创建成功
// ifindex ,prog_id, xdp_flags
ret = bpf_get_link_xdp_id(0, &prog_id, 0);
if (ret)
goto error_exit;
/* Initialize umem frame allocation */
// 初始化UMEM
for (i = 0; i < NUM_FRAMES; i++)
xsk_info->umem_frame_addr[i] = i * FRAME_SIZE;
xsk_info->umem_frame_free = NUM_FRAMES;
/* Stuff the receive path with buffers, we assume we have enough */
// 初始化RX队列
ret = xsk_ring_prod__reserve(&xsk_info->umem->fq,
XSK_RING_PROD__DEFAULT_NUM_DESCS,
&idx);
if (ret != XSK_RING_PROD__DEFAULT_NUM_DESCS)
goto error_exit;
for (i = 0; i < XSK_RING_PROD__DEFAULT_NUM_DESCS; i ++)
*xsk_ring_prod__fill_addr(&xsk_info->umem->fq, idx++) =
xsk_alloc_umem_frame(xsk_info);
xsk_ring_prod__submit(&xsk_info->umem->fq,
XSK_RING_PROD__DEFAULT_NUM_DESCS);
return xsk_info;
error_exit:
errno = -ret;
return NULL;
}定数输出xdp数据包数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24pthread_t stats_poll_thread;
int ret = pthread_create(&stats_poll_thread, NULL, stats_poll,xsk_socket);
static bool global_exit;
static void *stats_poll(void *arg)
{
unsigned int interval = 2;
struct xsk_socket_info *xsk = arg;
static struct stats_record previous_stats = { 0 };
previous_stats.timestamp = gettime();
/* Trick to pretty printf with thousands separators use %' */
setlocale(LC_NUMERIC, "en_US");
while (!global_exit) {
sleep(interval);
xsk->stats.timestamp = gettime();
stats_print(&xsk->stats, &previous_stats);
previous_stats = xsk->stats;
}
return NULL;
}从RX队列中poll数据,并进行处理(此章节未完成)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137rx_and_process(xsk_socket);
static void rx_and_process(struct xsk_socket_info *xsk_socket)
{
struct pollfd fds[2];
int ret, nfds = 1;
memset(fds, 0, sizeof(fds));
fds[0].fd = xsk_socket__fd(xsk_socket->xsk);
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
while(!global_exit) {
if ("skb-mode") {
ret = poll(fds, nfds, -1);
if (ret <= 0 || ret > 1)
continue;
}
handle_receive_packets(xsk_socket); //用户态处理xdp数据包核心函数
}
}
static void handle_receive_packets(struct xsk_socket_info *xsk)
{
unsigned int rcvd, stock_frames, i;
uint32_t idx_rx = 0, idx_fq = 0;
int ret;
rcvd = xsk_ring_cons__peek(&xsk->rx, RX_BATCH_SIZE, &idx_rx);
if (!rcvd)
return;
/* Stuff the ring with as much frames as possible */
stock_frames = xsk_prod_nb_free(&xsk->umem->fq,
xsk_umem_free_frames(xsk));
if (stock_frames > 0) {
ret = xsk_ring_prod__reserve(&xsk->umem->fq, stock_frames,
&idx_fq);
/* This should not happen, but just in case */
while (ret != stock_frames)
ret = xsk_ring_prod__reserve(&xsk->umem->fq, rcvd,
&idx_fq);
for (i = 0; i < stock_frames; i++)
*xsk_ring_prod__fill_addr(&xsk->umem->fq, idx_fq++) =
xsk_alloc_umem_frame(xsk);
xsk_ring_prod__submit(&xsk->umem->fq, stock_frames);
}
/* Process received packets */
for (i = 0; i < rcvd; i++) {
uint64_t addr = xsk_ring_cons__rx_desc(&xsk->rx, idx_rx)->addr;
uint32_t len = xsk_ring_cons__rx_desc(&xsk->rx, idx_rx++)->len;
if (!process_packet(xsk, addr, len))
xsk_free_umem_frame(xsk, addr);
xsk->stats.rx_bytes += len;
}
xsk_ring_cons__release(&xsk->rx, rcvd);
xsk->stats.rx_packets += rcvd;
/* Do we need to wake up the kernel for transmission */
complete_tx(xsk);
}
// 处理数据包核心逻辑部分
static bool process_packet(struct xsk_socket_info *xsk,
uint64_t addr, uint32_t len)
{
uint8_t *pkt = xsk_umem__get_data(xsk->umem->buffer, addr);
/* Lesson#3: Write an IPv6 ICMP ECHO parser to send responses
*
* Some assumptions to make it easier:
* - No VLAN handling
* - Only if nexthdr is ICMP
* - Just return all data with MAC/IP swapped, and type set to
* ICMPV6_ECHO_REPLY
* - Recalculate the icmp checksum */
if (false) {
int ret;
uint32_t tx_idx = 0;
uint8_t tmp_mac[ETH_ALEN];
struct in6_addr tmp_ip;
struct ethhdr *eth = (struct ethhdr *) pkt;
struct ipv6hdr *ipv6 = (struct ipv6hdr *) (eth + 1);
struct icmp6hdr *icmp = (struct icmp6hdr *) (ipv6 + 1);
if (ntohs(eth->h_proto) != ETH_P_IPV6 ||
len < (sizeof(*eth) + sizeof(*ipv6) + sizeof(*icmp)) ||
ipv6->nexthdr != IPPROTO_ICMPV6 ||
icmp->icmp6_type != ICMPV6_ECHO_REQUEST)
return false;
memcpy(tmp_mac, eth->h_dest, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(eth->h_dest, eth->h_source, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(eth->h_source, tmp_mac, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(&tmp_ip, &ipv6->saddr, sizeof(tmp_ip));
memcpy(&ipv6->saddr, &ipv6->daddr, sizeof(tmp_ip));
memcpy(&ipv6->daddr, &tmp_ip, sizeof(tmp_ip));
icmp->icmp6_type = ICMPV6_ECHO_REPLY;
csum_replace2(&icmp->icmp6_cksum,
htons(ICMPV6_ECHO_REQUEST << 8),
htons(ICMPV6_ECHO_REPLY << 8));
/* Here we sent the packet out of the receive port. Note that
* we allocate one entry and schedule it. Your design would be
* faster if you do batch processing/transmission */
ret = xsk_ring_prod__reserve(&xsk->tx, 1, &tx_idx);
if (ret != 1) {
/* No more transmit slots, drop the packet */
return false;
}
xsk_ring_prod__tx_desc(&xsk->tx, tx_idx)->addr = addr;
xsk_ring_prod__tx_desc(&xsk->tx, tx_idx)->len = len;
xsk_ring_prod__submit(&xsk->tx, 1);
xsk->outstanding_tx++;
xsk->stats.tx_bytes += len;
xsk->stats.tx_packets++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
完整代码:
在用户态输出xdp包数据,运行结果:
